Palo Alto Firewall (Version 7)¶
The purpose of this document is to detail the installation and configuration of an Lantronix Local Manager (LM) to manage and facilitate remote connectivity to a Palo Alto firewall.
Features¶
Supports Palo Alto firewalls running PAN-OS version 7 or higher.
Physical Connection¶
Connect a free serial port on the Local Manager to the Palo Alto's RS-232 console management port with a standard Cat-5 cable.
Recommended Configuration¶
For proactive monitoring of the Palo Alto's status, and to ensure the availability of backup configurations, it is recommended that:
- The Local Manager serial port connected to the Palo Alto is configured via the config init command
- Automatic backup of the configuration is scheduled
- The paloAltoStatus ruleset is scheduled
Configuring the Port¶
To configure the Local Manager for connection to a Palo Alto firewall, navigate to the port that the Palo Alto is connected to, run the command config init, and follow the prompts as below (substituting your Palo Alto's IP address):
[admin@LantronixLM (port1/4)]# config init
--- Enter New Values ---
description: Palo Alto firewall
make [native]: enhanced
management IP: 203.0.113.16
Configure dedicated ethernet port? (y/n) [n]:
command prompt [[#>]]:
login prompt [(ogin:\s]: (?<!(?:ast|uccessful)\s)[lL]ogin:\s
password prompt [assword:\s]: Password:\s
logout command [exit\r]:
wakeup command [\r]:
console username []: admin
console password []: ********
confirm password []: ********
Serial Bit Rate [9600]:
Serial Data Bit [8]:
Serial Parity [none]:
Serial Stop Bit [1]:
Serial Flow Control [none]:
Do you want to commit these changes? (y/n): y
Testing login will take a few moments...
Login successful; credentials are valid.
Scheduling default jobs
Testing job rulesMonitor
Job rulesMonitor was successful
Job rulesMonitor was scheduled
The default console settings for the Palo Alto firewall are 9600 bit rate, 8 serial data bit, no serial parity, serial stop bit 1, and no flow control.
Managing Configurations¶
Back up Configuration¶
The Lantronix Local Manager can save up to twenty backup images on its file system for use in restoring a configuration or pushing a configuration to a new Palo Alto. The file can be transferred to the LM via TFTP or SCP.
To save the Palo Alto's configuration to the LM, navigate to the port that the Palo Alto is connected to and run the either of the following commands, substituting the LM's IP address.
pull sftp -file running-config.xml "scp export configuration from running-config.xml to ${user}@${ip}:${path}" running-config current
pull tftp "tftp export configuration to 10.0.1.2 from running-config.xml" running-config.xml running-config current
Example:
[admin@LantronixLM]# port 1/4
Palo Alto firewall
[admin@LantronixLM (port1/4)]# pull tftp "tftp export configuration to 10.0.1.2 from running-config.xml" running-config.xml running-config current
Automatic Configuration Backup¶
To configure the Local Manager to back up the running-config of a Palo Alto firewall every three hours, use one of the following commands:
config schedule pullSftp "scp export configuration from running-config.xml to ${user}@${ip}:${path}" running-config current -d 10800
config schedule pullTftp "tftp export configuration to 10.0.1.2 from running-config.xml" running-config.xml running-config current -d 10800
Restore Configuration¶
There are multiple steps to restore a backup configuration to a Palo Alto firewall. The file may be transferred via SCP or TFTP.
First, navigate to the port the Palo Alto is connected to and stage the file to be restored as a candidate configuration:
Next, run one of the following commands, substituting the LM's IP address.
push sftp -file running-config.xml "scp import configuration ${user}@${ip}:${path} \r configure \r load config from running-config.xml \r commit \r exit" running-config candidate
push tftp "tftp import configuration 10.0.1.2/running-config.xml \r configure \r load config from running-config.xml \r commit \r exit" running-config.xml running-config candidate
Upon entering one of those commands, the LM will connect to the Palo Alto's CLI, transfer the candidate configuration, and apply the configuration.
Monitoring Palo Alto Status¶
Palo Alto Health Check Ruleset¶
The Local Manager can be configured to monitor the status of a managed Palo Alto using the PaloAltoChassisRules rule set. The LM will check the Palo Alto for environmental alarms and high CPU usage. High CPU usage or system heat will trigger an alarm on the LM.
To load the PaloAltoChassisRules rule set on the LM, copy and paste the following into the LM at the system level:
config rule no PaloAltoCPUCheck0
config rule PaloAltoCPUCheck0
action execute -pattern "(\d?\d\.\d?)%id" -command "set cli scripting-mode on\rshow system resources\r" -raw -multiline -setValue monitor CPUidle $1
conditions
true
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoCPUCheck1
config rule PaloAltoCPUCheck1
description a rule to send an alarm when CPU idle is below a certain number - adjust target as appropriate
action alarm GENERIC -a "CPU usage above 0%"
conditions
compare-value monitor CPUidle <= 99.9
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoMemoryCheck0
config rule PaloAltoMemoryCheck0
action execute -pattern "(\d*)k free" -command "set cli scripting-mode on\rshow system resources\r" -raw -multiline -setValue monitor MemoryFree $1
conditions
true
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoMemoryCheck1
config rule PaloAltoMemoryCheck1
description a rule to send an alarm when free memory is below a certain number - adjust target as appropriate
action alarm GENERIC -a "free memory below 1000000"
conditions
compare-value monitor MemoryFree <= 1000000
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoDiskCheck0
config rule PaloAltoDiskCheck0
action execute -pattern "(?m)(\d{1,3})% .*\v+^.* (\d{1,3})% .*\v+.* (\d{1,3})% .*(?:\v+.* (\d{1,3})% .*(?:\v+.* (\d{1,3})% .*(?:\v+.* (\d{1,3})% .*)?)?)?" -command "show system disk-space" -setValue monitor disk1usage $1 -setValue monitor disk2usage $2 -setValue monitor disk3usage $3 -setValue monitor disk4usage $4 -setValue monitor disk5usage $5 -setValue monitor disk6usage $6
conditions
true
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoDiskCheck1
config rule PaloAltoDiskCheck1
description a rule to send an alarm when disk usage is above a certain number - adjust target percentage as appropriate
action alarm GENERIC -a "disk usage over 80%"
action writeStatus DISK USAGE HIGH
conditions
compare-value monitor disk1usage >= 80 OR
compare-value monitor disk2usage >= 80 OR
compare-value monitor disk3usage >= 80 OR
compare-value monitor disk4usage >= 80 OR
compare-value monitor disk5usage >= 80 OR
compare-value monitor disk6usage >= 80
exit
exit
config ruleset no PaloAltoChassisRules
config ruleset PaloAltoChassisRules
rules
PaloAltoCPUCheck0 | PaloAltoCPUCheck1 | PaloAltoMemoryCheck0 | PaloAltoMemoryCheck1 | PaloAltoDiskCheck0 | PaloAltoDiskCheck1
exit
exit
To configure the Lantronix LM to use the PaloAltoChassisRules rule set to monitor a Palo Alto firewall, navigate to the port that the Palo Alto is connected to and run the following command:
Palo Alto High Availability Status Check¶
The following rules will check the Palo Alto's High Availability Status (not related to Control Center High Availability) and create an alarm if HA is not working or isn't set up.
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck001
config rule PaloAltoHACheck001
action setValue monitor haStage active
conditions
NOT has-value monitor haStage AND
compare-value monitor haState = active
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck002
config rule PaloAltoHACheck002
action setValue monitor haStage passive
conditions
NOT has-value monitor haStage AND
compare-value monitor haState = passive
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck0
config rule PaloAltoHACheck0
action execute -pattern "(active|passive|suspended|non-functional|not)" -command "set cli scripting-mode on\r show high-availability state\r" -raw -setValue monitor haState $1
conditions
true
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck1
config rule PaloAltoHACheck1
action writeStatus HA-ACTIVE
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = active
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck2
config rule PaloAltoHACheck2
action writeStatus HA-PASSIVE
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = passive
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck3
config rule PaloAltoHACheck3
action alarm GENERIC -a "HA suspended"
action writeStatus HA-SUSPENDED
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = suspended
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck4
config rule PaloAltoHACheck4
action alarm GENERIC -a "Palo Alto shows NON-FUNCTIONAL status"
action writeStatus NON-FUNCTIONAL
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = non-functional
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck5
config rule PaloAltoHACheck5
action alarm GENERIC -a "Palo Alto HA not enabled"
action writeStatus HA NOT ENABLED
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = not
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck6
config rule PaloAltoHACheck6
action setValue monitor haStage passive
action alarm GENERIC -a "HA changed to passive"
action event GENERIC -a "HA changed to passive
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = passive AND
compare-value monitor haStage = active
exit
exit
config rule no PaloAltoHACheck7
config rule PaloAltoHACheck7
action setValue monitor haStage active
action alarm GENERIC -a "HA changed to active"
action event GENERIC -a "HA changed to active"
conditions
compare-value monitor haState = passive AND
compare-value monitor haStage = active
exit
exit
config ruleset no PaloAltoHACheck
config ruleset PaloAltoHACheck
rules
PaloAltoHACheck001 | PaloAltoHACheck002 | PaloAltoHACheck0 | PaloAltoHACheck1 | PaloAltoHACheck2 | PaloAltoHACheck3 | PaloAltoHACheck4 | PaloAltoHACheck5 | PaloAltoHACheck6 | PaloAltoHACheck7
exit
exit
To schedule the above rules, run the following command:
You can also combine this ruleset with the Health Status check ruleset:
Connecting to the Web Interface¶
Port Forwarding¶
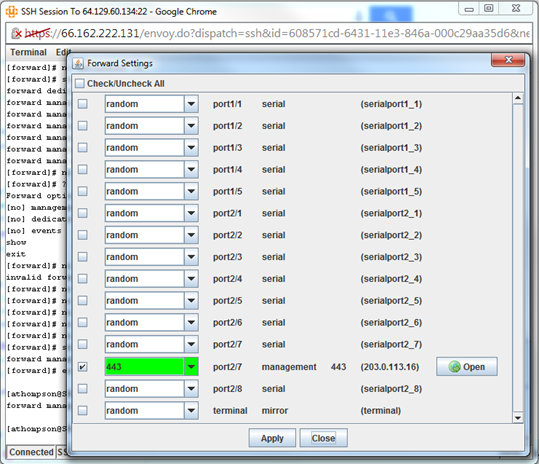
The Local Manager can facilitate connections to the Palo Alto's web interface using the port forwarding feature. Run configure protocol forward on the port the Palo Alto is connected to and add an entry as below:
[admin@LantronixLM (port1/4)]# config protocol forward
[forward]# management 443 https
[forward]# exit
Users may now connect to the web interface through an SSH tunnel using the port forwarding feature. In the Lantronix native Terminal Application on the Control Center, click Terminal, then Forward. Select the Palo Alto's port, enter 443 for the port number, and click Apply. Now, port 443 on 127.0.0.1 on your workstation will connect through the SSH tunnel created by the LM to the web interface on the Palo Alto.