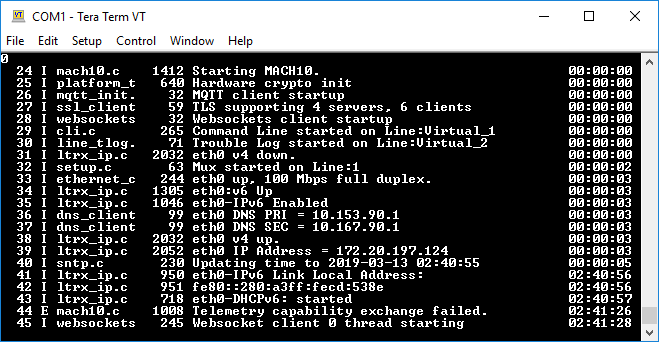
Use Cases¶
The following example shows you how you can use the XPort EDGE.
Access CLI and Trouble Log over mux, configuring via XML¶
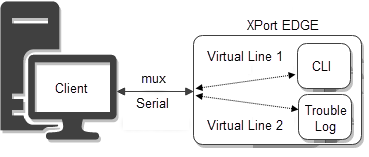
This example uses CLI to import XML configuration. The import configures Line 1 for mux, Virtual Line 1 for CLI, and Virtual Line 2 for the trouble log. It then shows how to use both those virtual lines over mux. Because it uses CLI to import the XML configuration, it assumes Line 1 is already enabled and using the Command Line protocol, as is default.
Step 1 - Import XML configuration
- Connect the XPort EDGE to a PC using a serial cable.
- On the PC, open a terminal such as Tera Term and connect to the device using serial. This example uses Tera Term.
- Send
configto enter the config level. - Send
Line 1to enter the config Line 1 level. - Send
Flow Control Softwareto set Flow Control to Software. Flow Control is required to import XML configuration.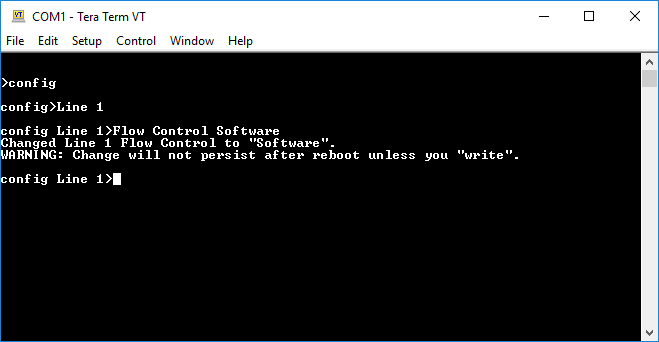
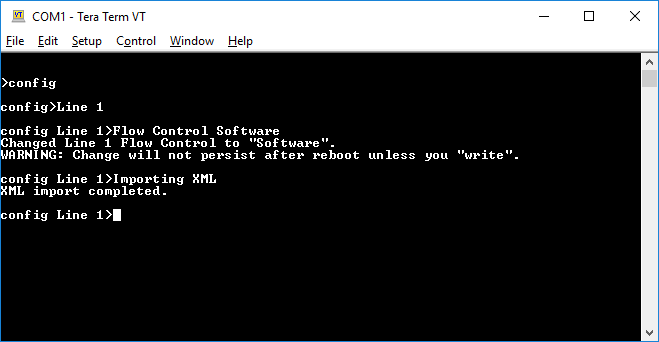
- Paste the following XML in Tera Term.
<?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
<!-- Automatically generated XML -->
<!DOCTYPE configrecord [
<!ELEMENT configrecord (configgroup+)>
<!ELEMENT configgroup (configitem+)>
<!ELEMENT configitem (value+)>
<!ELEMENT value (#PCDATA)>
<!ATTLIST configrecord version CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configgroup name CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configgroup instance CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configitem name CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST configitem instance CDATA #IMPLIED>
<!ATTLIST value name CDATA #IMPLIED>
]>
<configrecord version = "0.1.0.1">
<configgroup name = "Line" instance = "1">
<configitem name = "Name">
<value></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Interface">
<value>RS232</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "State">
<value>Enabled</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Protocol">
<value>Mux</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Baud Rate">
<value>9600 bits per second</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Parity">
<value>None</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Data Bits">
<value>8</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Stop Bits">
<value>1</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Flow Control">
<value>Software</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Gap Timer">
<value><Four Character Periods></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Threshold">
<value>56 bytes</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Push">
<value></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
<configgroup name = "Line" instance = "Virtual_1">
<configitem name = "Name">
<value></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "State">
<value>Enabled</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Protocol">
<value>Command Line</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Gap Timer">
<value><Four Character Periods></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Threshold">
<value>56 bytes</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Push">
<value></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
<configgroup name = "Line" instance = "Virtual_2">
<configitem name = "Name">
<value></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "State">
<value>Enabled</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Protocol">
<value>Trouble Log</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Gap Timer">
<value><Four Character Periods></value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Threshold">
<value>56 bytes</value>
</configitem>
<configitem name = "Push">
<value></value>
</configitem>
</configgroup>
</configrecord>
Step 2 - Use mux to access CLI on Virtual Line 1
- Disconnect Tera Term and reconnect to the xPico 200 Series to access mux on Line 1.
- Type
1v1and press ENTER to connect to Virtual Line 1 as instance 1. Note that mux does not echo input characters.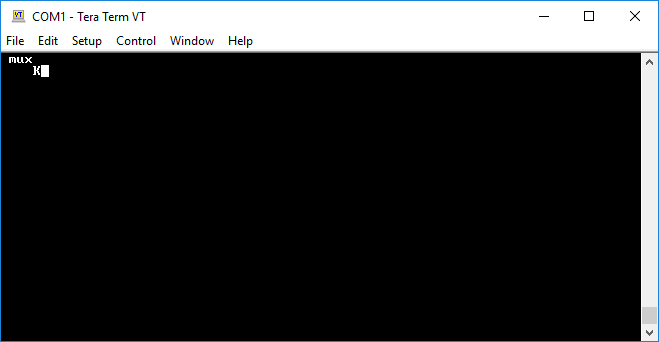
- Type
1sb~and press ENTER to prepare to send data. The~is specified as the escape character.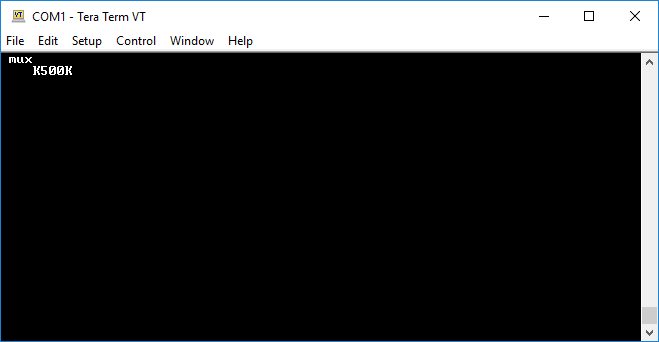
- Type
?~and press ENTER to prepare the?CLI command. The~followed by a newline terminates the data. Note that a newline is not being sent to the Virtual Line 1 because one isn't needed after the?command.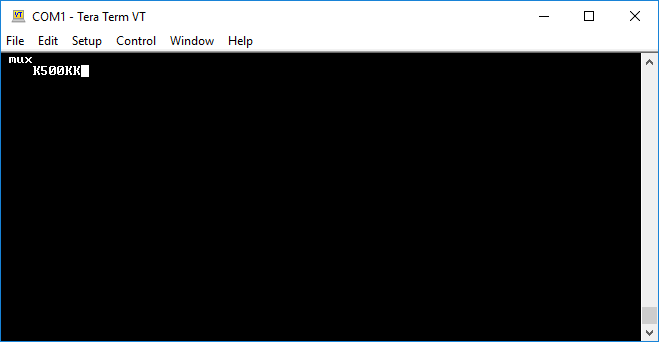
- Type
1pand press ENTER to send the prepared data.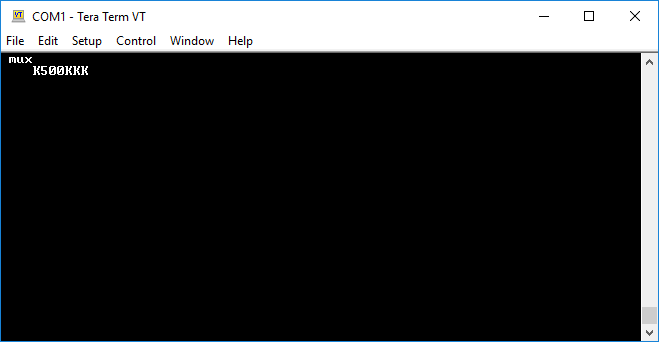
- Type
1rb~2000and press ENTER to receive data. You will see the results of the?command.
- Type
1sb~and press ENTER to prepare to send data again.
- Type
configand press ENTER to prepare theconfigcommand with a newline. Unlike the?command, theconfigcommand requires a newline. - Type
~and press ENTER to send the escape character and indicate the end of the data being prepared.
- Type
1pand press ENTER to send the prepared data.
- Type
1rb~2000and press ENTER to receive data. You can repeat steps 7 through 10 to send CLI commands over mux to the Command Line on Virtual Line 1.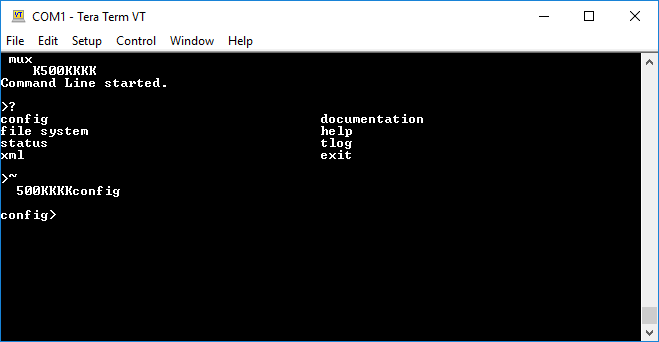
Step 3 - Use mux to access the trouble log on Virtual Line 2
- Type
2v2and press ENTER to connect to Virtual Line 2 as instance 2.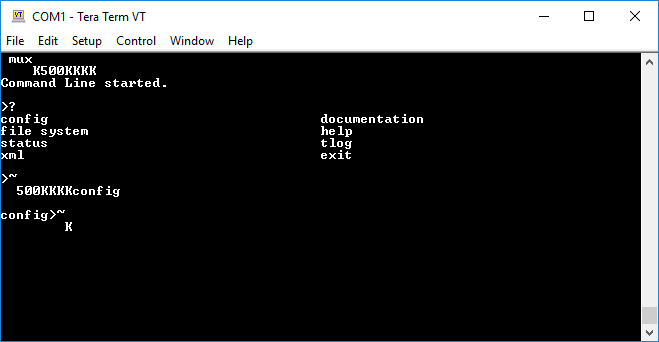
- Type
2rb~2000to receive data from the trouble log.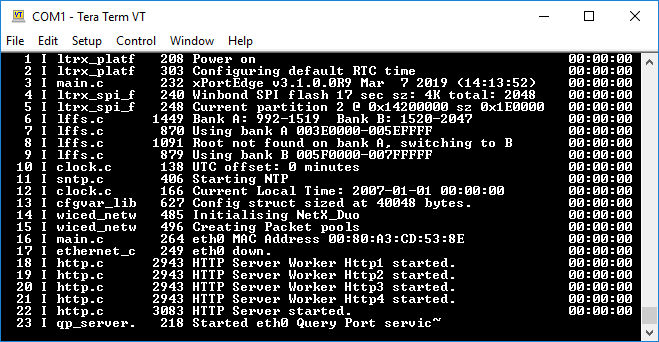
- If there is more data, repeat step 2 as necessary to receive additional data from the trouble log.